
오늘 학습 키워드
유니티 심화 팀 프로젝트
오늘 학습 한 내용을 나만의 언어로 정리하기
Behaviour Tree 만들기
- Behaviour Tree는 FSM에서 확장성을 더 키운 버전으로 보임
기본 시스템
- Behaviour Tree는 여러 개의 노드로 구성됨
- 노드의 종류
- Leaf Node : 실제 동작(Action)을 하거나 조건(Condition) 검사를 함
- Composite Node : 자식 노드들을 실행함
- Sequence Node : 자식 노드들을 순서대로 실행하면서 하나라도 실패가 나오면 실패.
- Selector Node : 자식 노드들을 순서대로 실행하다가 하나라도 성공하면 반환
- Decorator Node : 실행 조건을 감싸거나 반복 제어
기본 시스템 코드 구현
-
기본 노드 만들기
-
각각의 노드는 세 가지 상태를 가짐. Running, Success, Failure
// NodeState.cs
public enum NodeState
{
Running,
Success,
Failure
}- 모든 노드는 기본적으로 실행하는 부분이 있음
// Node.cs
public abstract class Node
{
protected NodeState state;
public NodeState State => state;
public abstract NodeState Evaluate(); // 실행부
}- Sequence 노드는 모든 자식 노드가 실행이 완료되고 성공이어야 성공임
public class Sequence : Node
{
private List<Node> children;
// 자식 노드 받아오기
public Sequence(List<Node> children)
{
this.children = children;
}
public override NodeState Evaluate()
{
bool anyRunning = false; // 실행 중인 노드가 있는지 체크하는 부분
foreach (var child in children)
{
switch (child.Evaluate())
{
// 하나라도 실패하면 안됨.
case NodeState.Failure:
state = NodeState.Failure;
return state;
// 성공하면 다음 자식으로 이동
case NodeState.Success:
continue;
// 어떤 자식 노드가 실행 중이라면 이 Sequence 노드의 상태도 실행 중임.
case NodeState.Running:
anyRunning = true;
break;
}
}
state = anyRunning ? NodeState.Running : NodeState.Success;
return state;
}
}- Selector 노드는 하나의 노드가 성공이어도 성공임
public class Selector : Node
{
private List<Node> children;
public Selector(List<Node> children)
{
this.children = children;
}
public override NodeState Evaluate()
{
bool anyRunning = false; // 실행 중인 노드가 있는지 체크하는 부분
foreach (var child in children)
{
switch (child.Evaluate())
{
// 실패하면 다음 자식으로 이동
case NodeState.Failure:
continue;
// 하나라도 성공하면 selector는 성공
case NodeState.Success:
state = NodeState.Success;
return state;
// 실행 중이면 그게 우선
case NodeState.Running:
anyRunning = true;
break;
}
}
state = anyRunning ? NodeState.Running : NodeState.Failure;
return state;
}
}- Behaviour Tree는 루트 노드의 Evaluate를 지속적으로 불러주면 됨
public class BehaviourTree
{
private Node root;
public BehaviourTree(Node root)
{
this.root = root;
}
public void Tick()
{
root.Evaluate();
}
}시스템 코드 수정
- Sequence, selector는 Running 상태인 애들을 다시 부를 수 있도록 수정
// Sequence.cs
public class Sequence : Node
{
private List<Node> children;
private int currentIndex = 0;
// 자식 노드 받아오기
public Sequence(List<Node> children)
{
this.children = children;
}
public override NodeState Evaluate()
{
while (currentIndex < children.Count)
{
NodeState result = children[currentIndex].Evaluate();
switch (result)
{
// Sequence는 하나만 실패해도 전체 실패임
case NodeState.Failure:
currentIndex = 0;
state = NodeState.Failure;
return state;
// Running 인 경우에는 다음에 얘부터 실행하도록
case NodeState.Running:
state = NodeState.Running;
return state;
case NodeState.Success:
currentIndex++; // 다음 노드로 진행
break;
}
}
currentIndex = 0;
state = NodeState.Success;
return state;
}
}// Selector.cs
public class Selector : Node
{
private List<Node> children;
private int currentIndex = 0; // 마지막으로 실행한 자식 인덱스 기억
public Selector(List<Node> children)
{
this.children = children;
}
public override NodeState Evaluate()
{
while (currentIndex < children.Count)
{
NodeState result = children[currentIndex].Evaluate();
switch (result)
{
case NodeState.Success:
// Selector는 하나라도 성공하면 전체 성공
currentIndex = 0;
state = NodeState.Success;
return state;
case NodeState.Running:
// 실행 중이면 다음 틱에도 같은 자식부터 실행
state = NodeState.Running;
return state;
case NodeState.Failure:
currentIndex++; // 다음 자식으로 진행
break;
}
}
// 모든 자식이 실패했을 때
currentIndex = 0;
state = NodeState.Failure;
return state;
}
}개발 시작
- 시스템 구성도
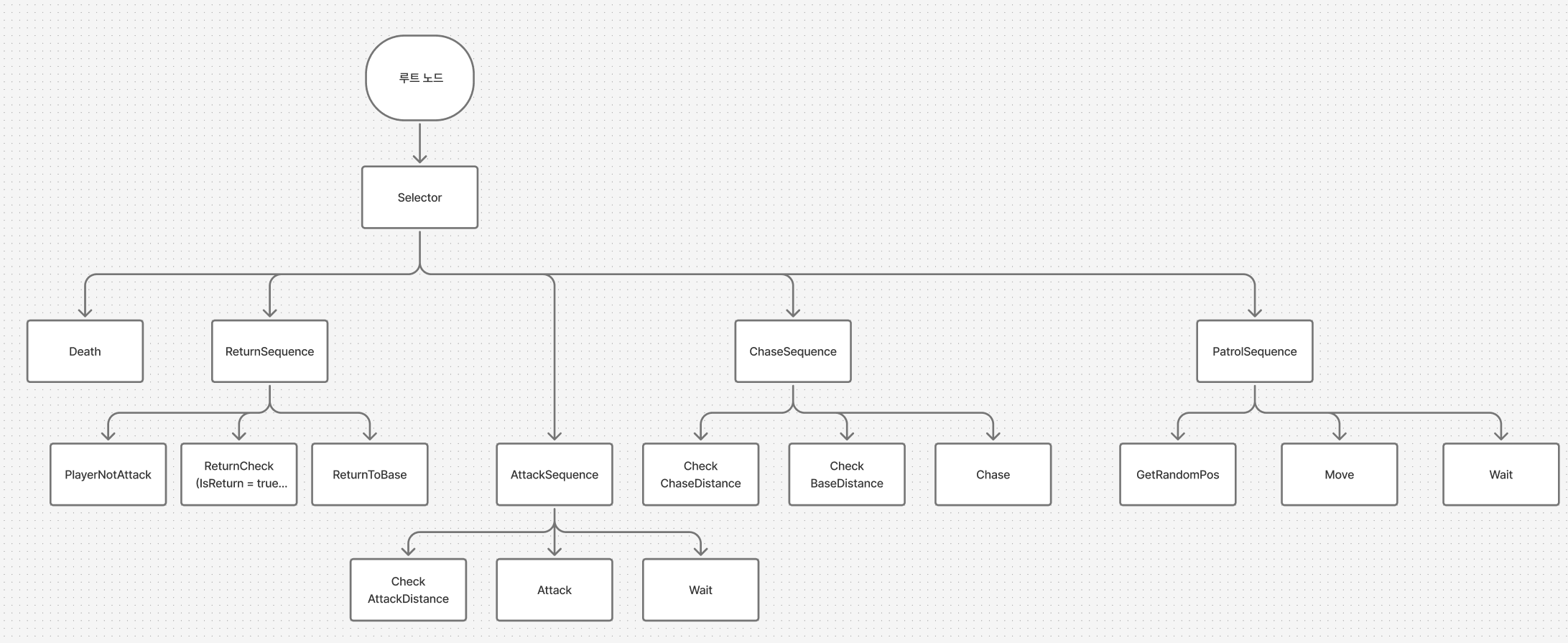
- 여기서 일단 ChaseSequence랑 PatrolSequence를 실행할 예정
Chase Sequence
// CanRecogPlayerNode.cs
public class CanRecogPlayerNode : Node
{
private Monster monster;
private Transform player;
private float distance;
public CanRecogPlayerNode(Monster monster, Transform player)
{
this.monster = monster;
this.player = player;
}
public override NodeState Evaluate()
{
distance = Vector2.Distance(monster.transform.position, player.position);
// 몬스터 인식 거리 내부이면 성공
if (distance <= monster.Recognize)
{
Debug.Log($"Can Recognize Player");
state = NodeState.Success;
}
else
state = NodeState.Failure;
return state;
}
}// ChasePlayerNode.cs
public class ChasePlayerNode : Node
{
private Monster monster;
private Transform player;
private float distance;
public ChasePlayerNode(Monster monster, Transform player)
{
this.monster = monster;
this.player = player;
}
public override NodeState Evaluate()
{
distance = Vector2.Distance(monster.transform.position, player.position);
// 공격 가능 범위까지 왔으면 성공
if (distance <= monster.AttackRange)
{
Debug.Log($"Can Attack Player");
state = NodeState.Success;
return state;
}
// 너무 멀어졌으면 실패
else if (distance >= monster.Recognize)
{
Debug.Log($"Fail to chase player");
state = NodeState.Failure;
return state;
}
// 성공/실패 아니면 진행 중
else
{
monster.MoveToTarget(player.position);
state = NodeState.Running;
return state;
}
}
}Patrol Sequence
// GetRandomPositionNode.cs
public class GetRandomPositionNode : Node
{
private Monster monster;
public GetRandomPositionNode(Monster monster)
{
this.monster = monster;
}
public override NodeState Evaluate()
{
if (!monster.isMoving)
{
monster.SetRandomDestination();
Debug.Log($"New Position : {monster.Destination.x}");
}
state = NodeState.Success;
return state;
}
}// MoveNode.cs
public class MoveNode : Node
{
private Monster monster;
public MoveNode(Monster monster)
{
this.monster = monster;
}
public override NodeState Evaluate()
{
if (monster.MoveToDestination())
{
Debug.Log("Move Done");
state = NodeState.Success;
}
else
{
state = NodeState.Running;
}
return state;
}
}// WaitNode.cs
// 확장 가능하도록 설정함
public class WaitNode : Node
{
private float waitTime;
private float startTime;
public WaitNode(float waitTime)
{
this.waitTime = waitTime;
startTime = 0;
}
public override NodeState Evaluate()
{
if (startTime == 0)
{
startTime = Time.time;
}
if (Time.time - startTime >= waitTime)
{
startTime = 0;
state = NodeState.Success;
return state;
}
state = NodeState.Running;
return state;
}
}내일 학습 할 것은 무엇인지
- 나머지 Sequence들도 만들어야함